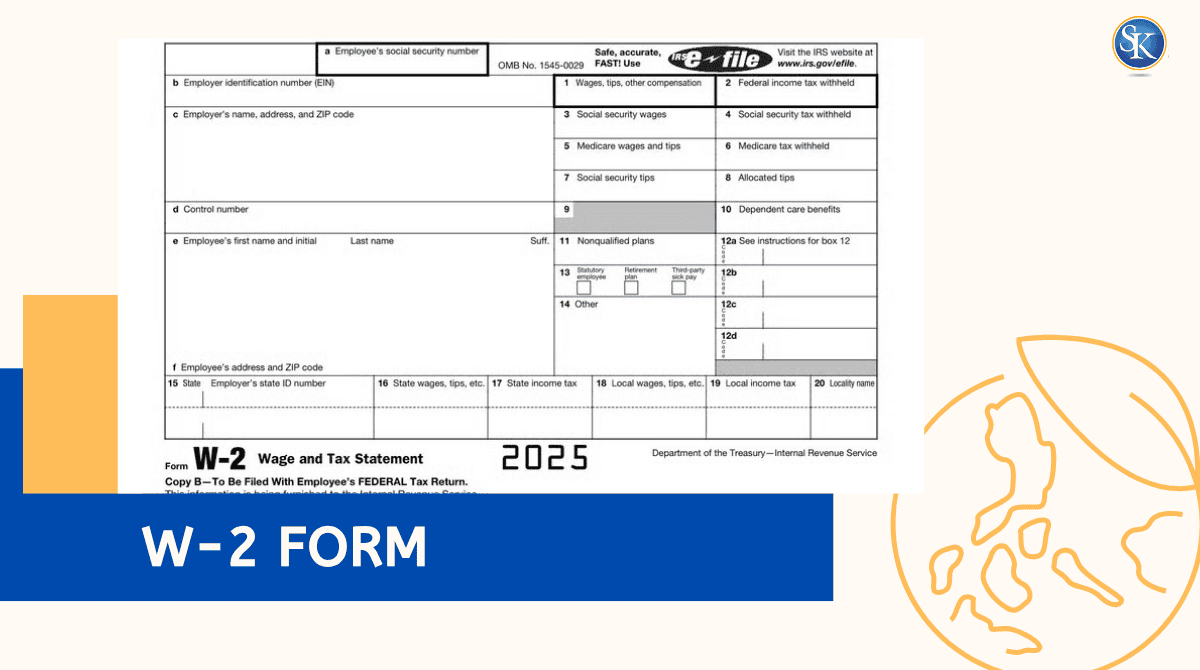
What is W-2 form and How to Read It: Wage and Tax Statement
The W-2 form, also called the Wage and Tax Statement, is one of the most important tax documents you’ll receive each year. Employers send it to both you and the IRS to show how much money you earned and how much tax was withheld from your paycheck. Understanding your W-2 helps you file your taxes correctly and avoid mistakes that could delay your refund.
For example: if your employer withheld $5,000 in federal tax during the year, you’ll see that amount clearly listed in Box 2 of your W-2.
What is the meaning of W-2?
What Information Is on a W-2 Form?
Your W-2 contains several key sections:
-
Employee information: Your name, address, and Social Security Number.
-
Employer information: Company name, EIN (Employer Identification Number), and address.
-
Wages: Total pay including salary, tips, and bonuses.
-
Taxes withheld: Federal, state, and local income tax taken from your pay.
-
Benefits & contributions: Items like retirement plan contributions, health insurance, and other deductions.
Example: If you earned $50,000 and contributed $2,000 to a 401(k), your W-2 will show $48,000 in taxable wages (Box 1).
Explore: Top Accounting and Bookkeeping Services in Florida, US
How Does W-2 Form Works?
-
Employers must issue your W-2 by January 31 every year.
-
A copy goes to the IRS and Social Security Administration (SSA).
-
You use it to file your Form 1040 tax return.
-
Always check it for errors, incorrect Social Security numbers or wages can delay your refund.
If anything looks wrong, contact your employer right away to request a corrected form called W-2c.
Why Are W-2 Forms Important?
The W-2 form is more than just a yearly document it’s proof of your income and the taxes you’ve already paid. It helps you file an accurate tax return and ensures the IRS has the same records as your employer.
When you use your W-2 to complete your tax return, it shows:
-
How much you earned in wages, tips, and bonuses
-
How much federal and state tax was withheld
-
Contributions made toward Social Security, Medicare, and retirement plans
If your W-2 is missing or inaccurate, your refund or filing could be delayed. Keeping copies of your W-2 forms is also helpful when applying for loans, mortgages, or financial aid, since lenders often use them to verify income.
When Are W-2s Sent Out?
By law, employers must send W-2 forms to employees no later than January 31 each year. This gives you enough time to prepare and file your taxes before the April 15 deadline.
You might receive your W-2 in one of three ways:
-
By mail: the traditional method sent to your home address
-
Electronically: through your company’s HR or payroll portal
-
By hand: if your employer distributes them in person
If you leave a job before year-end, your employer still has until January 31 of the next year to issue your W-2 for that employment period.
Keeping your mailing and email information updated helps avoid delays.
Who Receives a Form W-2?
Every employee who earns wages from a U.S. employer must receive a W-2. That includes both full-time and part-time workers who had taxes withheld from their paychecks.
However, independent contractors and self-employed workers do not receive a W-2. Instead, they get a Form 1099-NEC, which reports income paid without tax withholding. If you worked multiple jobs, you’ll receive a separate W-2 from each employer. You must include all of them when filing your tax return, since each reports part of your yearly income.
What If You Don’t Receive a W-2 Form?
If you haven’t received your W-2 by mid-February, here’s what to do:
-
Contact your employer or HR department and ask if it was mailed or if there’s an electronic copy available.
-
Verify your address. Incorrect mailing information is a common cause of delays.
-
Wait a few more days postal delays can happen in January.
If you still don’t get it, you can:
-
Call the IRS at 1-800-829-1040 to report a missing W-2.
-
File your tax return using Form 4852 (Substitute for Form W-2) if you can’t obtain it in time.
Keep copies of your last pay stub it can help you estimate your earnings and taxes withheld when filling out Form 4852.
What If You Find an Error on Your W-2 Form?
Always check your W-2 carefully before filing your tax return. Mistakes like misspelled names, wrong Social Security numbers, or incorrect income figures can lead to IRS processing issues.
If you notice an error:
-
Contact your employer immediately they must issue a corrected form, called a Form W-2c (Corrected Wage and Tax Statement).
-
Wait for the corrected version before filing your tax return to ensure accuracy.
-
Keep both copies (the original and the corrected one) for your records.
Common errors include:
-
Wrong address or SSN
-
Incorrect tax withholdings
-
Missing benefit or retirement contributions
If the employer doesn’t respond or no correction is made, contact the IRS for guidance. A tax professional, such as SK Financial CPA, can also help verify whether a correction is required before you file.
How to Read a W-2 Form?
|
Box No. |
What It Shows |
Why It Matters |
|
Box 1 |
Total taxable wages, tips, and bonuses |
This is your total income before taxes. |
|
Box 2 |
Federal income tax withheld |
The total amount already paid to the IRS. |
|
Boxes 3 & 4 |
Social Security wages & tax withheld |
Used for Social Security benefit tracking. |
|
Boxes 5 & 6 |
Medicare wages & tax withheld |
Helps fund your Medicare benefits. |
|
Box 12 |
Special codes (401k, health coverage, etc.) |
Each code (A–ZZ) shows extra benefits or deductions. |
Tip: Keep every W-2 for at least three years in case of an IRS review or future loan application.
Conclusion
Your W-2 is more than a form it’s your yearly financial snapshot. Understanding it helps you file your taxes correctly and know where your money went. Always double-check every box for accuracy, and if something doesn’t look right, talk to your employer or a CPA.
If you need help reading or filing your W-2. Book a free consultation with our CPAs that will review your W-2, explain your taxes, and help you avoid costly mistakes.
FAQs
1. What is a W-2 form?
A W-2 shows how much you earned and how much tax your employer withheld.
2. When will I get my W-2 form?
Employers must send it by January 31 each year.
3. What if I don’t receive my W-2?
Ask your employer first. If you still don’t get it by mid-February, contact the IRS.
4. What if there’s an error on my w2 form?
Tell your employer right away. They’ll issue a corrected form W-2c.
5. Can I file without a W-2 form?
Yes, using Form 4852, but it’s best to wait for your actual W-2 for accuracy.
6. What are the most important boxes?
Boxes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 they show your income and taxes paid.
7. What does Box 12 mean?
Box 12 lists codes for benefits or contributions, like retirement savings (Code D).
8. What if I worked for more than one employer?
You’ll get a separate W-2 from each employer use all of them when filing.
9. Can I get my W-2 form online?
Many companies provide digital copies through payroll portals. Check with HR.
10. How does a W2 form affect my tax return?
It determines your taxable income and refund amount.
Follow SKFinancial on Facebook / Twitter / Linkedin / Youtube for updates.












