What Is a W-9 Form? How to file and who can file
A W-9 is an IRS form a business requests from non-employees (freelancers, contractors, vendors) to collect your name, address, and TIN (SSN or EIN). The payer uses it to prepare 1099 forms at year-end. The W-9 doesn’t report income and doesn’t withhold tax it’s just your ID and certification.
Best and reliable bookkeeping and accounting services in FL,US
What is a W-9 Form?
The W-9 (“Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification”) gives a payer the exact details they need legal name, business name (if any), address, and TIN so they can correctly report payments to the IRS, typically on a Form 1099.
-
Who asks for it? Clients, platforms, banks, title companies, and anyone who must issue a 1099 or verify your TIN.
-
What it’s not: It’s not a bill, not a tax return, and not a form you send to the IRS.
W-9 vs W-4 vs W-8: What’s the Difference?
|
Form |
Who uses it |
Main purpose |
Withholding? |
|
W-9 |
U.S. persons who are not employees |
Give TIN and certify info for 1099 reporting |
No (but wrong/missing TIN can trigger backup withholding) |
|
W-4 |
Employees |
Tell employer how much to withhold from wages |
Yes (regular payroll withholding) |
|
W-8 (series) |
Non-U.S. persons/entities |
Claim foreign status/treaty benefits |
Withholding rules vary |
When You’ll Be Asked for a W-9
You’ll typically complete a W-9 when you:
-
Start freelance or contractor work for a new client.
-
Work via a marketplace/platform that issues 1099-K/1099-NEC.
-
Open bank/brokerage accounts that pay interest or dividends.
-
Receive prizes/awards, referral bonuses, or other miscellaneous income.
-
Close a real-estate deal (escrow/title may request it).
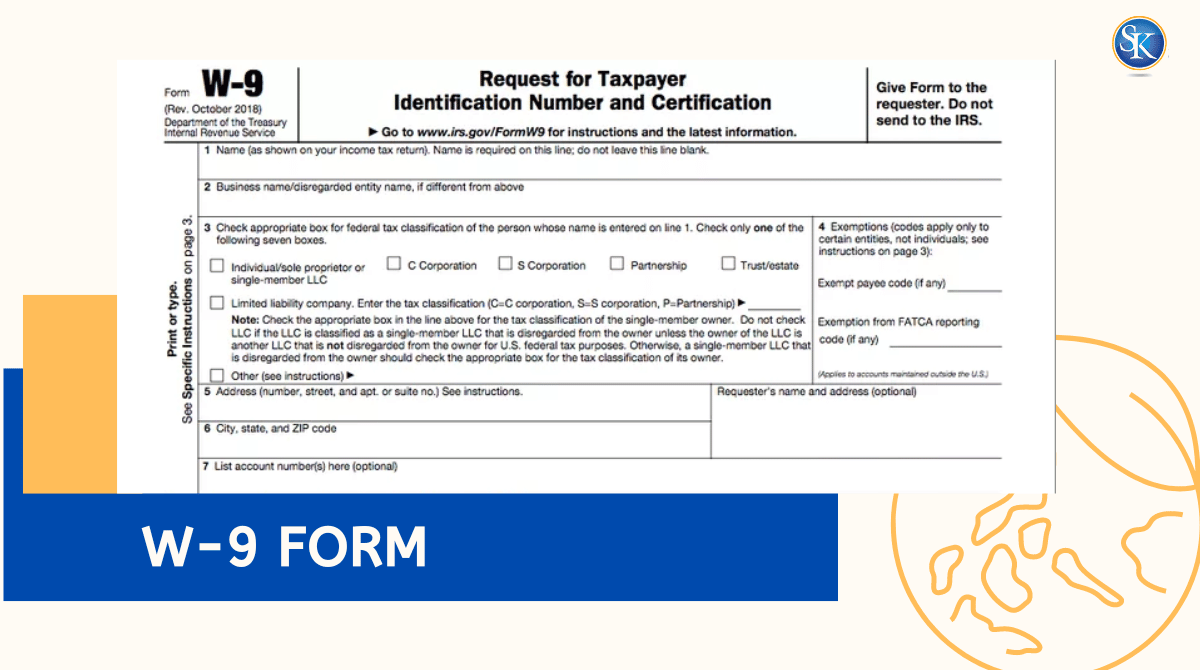
How to Fill Out Form W-9 (Step by Step)
1) Name & business name
Use your legal name (as on your tax return). If you have a business name/DBA, add it on the second line.
2) Federal tax classification
Select Individual/sole proprietor, LLC, C-corp, S-corp, Partnership, Trust/Estate, etc. Choose the one that matches your tax return.
3) Exemptions (most leave blank)
Only enter codes if you’re an exempt payee or subject to FATCA reporting (rare for most individuals).
4) Address
Enter the mailing address you use on your tax return so payers’ 1099s reach you.
5) TIN (SSN or EIN)
Individuals usually give an SSN; businesses often give an EIN. Use one TIN that matches the name in line 1.
6) Certification (signature)
Sign and date. You’re certifying your TIN is correct and you’re not subject to backup withholding (unless you are see next section).
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Using a nickname or a business name that doesn’t match your tax return.
-
Mismatching name and TIN (causes 1099 name/TIN mismatch notices).
-
Leaving the form unsigned.
-
Sending by insecure methods (emailing a raw PDF without encryption).
-
Forgetting to update when your address or entity type changes.
Backup Withholding (24%) & Security Tips
-
If you give a wrong or missing TIN, the payer may need to withhold 24% of payments (backup withholding) and send it to the IRS.
-
Protect your data Only send a W-9 to legitimate requesters. Use encrypted email, secure portals, or hand delivery. Keep a copy.
Who Should Fill Out a W-9?
-
Independent contractors, freelancers, gig workers, single-member LLCs.
-
Vendors and service providers paid outside payroll.
-
U.S. persons/entities receiving interest/dividends, prizes, or settlement payments.
Employees don’t fill out W-9s employees use W-4.
W-9 and 1099: How They Connect
Your W-9 details feed directly into the payer’s. 1099-NEC/1099-MISC/1099-INT/1099-DIV/1099-K at year-end. If your name/TIN is wrong on the W-9, the 1099 may be wrong and you may get an IRS notice.
Need help with contractor tax forms?
Unsure whether to use SSN vs EIN, or how your LLC should fill the W-9? Our team at SK Financial CPA can review your setup in minutes and help you avoid backup withholding and 1099 errors.
FAQs
What is a W-9 used for?
To give a payer your name, address, and TIN so they can issue a 1099.
Do I send the W-9 to the IRS?
No. You send it only to the requester (client, platform, bank), not the IRS.
I’m an employee do I fill a W-9?
No. Employees use W-4. W-9 is for non-employees.
Can I use my EIN instead of my SSN?
Yes, if it matches the name you put on line 1 and reflects how you file taxes.
What happens if I refuse to provide a W-9?
The payer may apply 24% backup withholding and may stop paying until you provide it.
Is a digital signature okay?
Yes, if the requester accepts it and the signature is legible/verifiable.
Do I need a new W-9 every year?
Not unless your name, address, or TIN changes or the payer asks for an update.
I’m not a U.S. person do I use W-9?
No. Use a W-8 form (such as W-8BEN/W-8BEN-E) instead.
Follow SKFinancial on Facebook / Twitter / Linkedin / Youtube for updates.














